Group dynamics
Group is made up 2 or more people that are communicating
with each other in a manner that each person influences or is influenced by
other team mates.
Group development:
The development of a group goes through these 4 stages:
- Forming
- Storming
- Norming
- Performing
Forming is when the team decides to meet and they all assess
the strengths and weaknesses of the whole group. Then they start to form
relationships and identify roles within group.
Storming is when conflict develops between the team members
and needs to be resolved so that the group can move forward. This can be
important as there will be a lot of stress involved or others may try to get a
more important role.
Norming is conflict replaced by co-operation and group moves
towards common goals. All the group members contribute in group decisions so
they have to agree or disagree to what they are discussing about.
Performing is progress and functioning as a group as well as
working towards the goals and achievement.
Steiner’s
model of group effectiveness:
Steiner's model was put up to explain group effectiveness. This model explains the relationship between the interactive group and it's performance in sport.
Steiner's model:
Actual productivity = potential productivity - losses due to faulty processes
Actual productivity refers to the team effort, how the team performs in the sport they are playing. Potential productivity refers to the individual skills and ability of each athlete in the team. For example, if a cricket team had 5 best fast bowlers who have taken the highest amount of wickets and 6 best batsmen who have scored really high runs then their team will be the best because the players in the team have good knowledge of the sport and understand their job in the sport as well as having good abilities and skills.
Loses due to faulty processes refers to the problems that can come in their way as a group. These problems may stop the whole team from progressing ahead and reaching their potential performance. Faulty processes may include loss of coordination, no communication among team mates.
Ringelman effect
The Ringelman effect suggests that as the size of the group increases the individual productivity decreases. This is not caused by co-ordinational loss, it is often because of motivational loss. Motivational losses occur when individuals are not being told when they are doing something good or something bad. Athletes hide behind other athletes in the team and get away with less effort and poor performance.
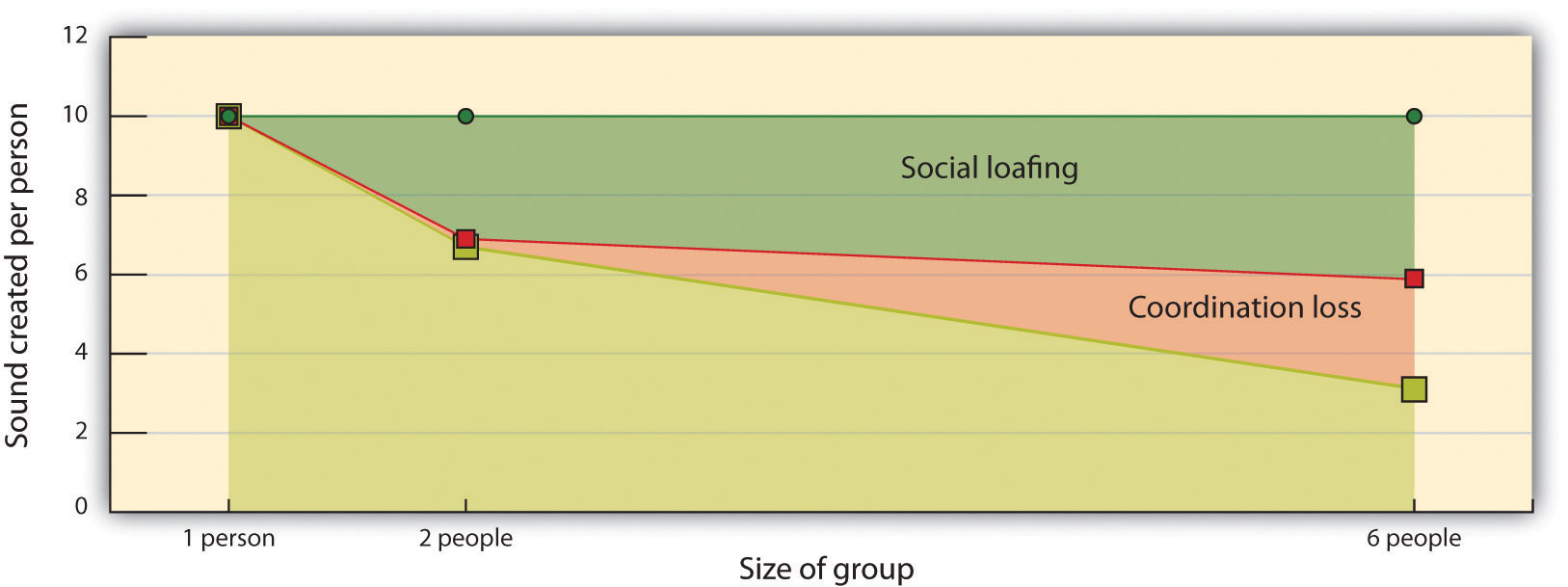
Social loafing
Social loafing is when there is loss of individual effort in a group due to reduction in motivation. An athlete's performance drops when there is motivational loss. Individuals feel they are not putting in enough effort for the whole group therefore, they don't bother putting in 100% effort. Individuals who fall in the social loafing category tend to be less confident and highly anxious, this may show that they are afraid of failing in the activity or sport they are playing. Some athletes display social loafing and may not put in full effort and may decide not to participate to avoid failure or on the other side they may feel that their contribution may not allow the team to progress or doesn't make a difference to the whole team therefore, they decide not to participate at all.
Interactive and co-active groups
Interactive team requires team members to work with the whole team in order to be a successful team and have successful performance. The successful performance depends on the co-ordination and interaction of each team member and the relationship among each other. An example of this would be a cricket team, to be able to be successful they need to have good co-ordination and interaction between themselves because their performance will effect the whole group. Where as in the IPL one country may not like players from the other team so they may decide not to talk to them but as they are professional players they don't show it on the ground by not passing the ball to the specific player.
Co-active team require individuals to achieve success in their individual games. This has to be done to improve the teams overall performance or achieve overall team success. Team members do not interact during the game or between the performance their is loss of co-ordination which may not have impact on some performers and they may continue playing individually.
Cohesion
Task cohesion is how well the team or the team members work together to achieve common goals and objectives.
Social cohesion refers to how well the team members enjoy each other's presence. In recreational games, all the players may get on with each other and enjoy the game no matter who wins or loses the game.
Both types of cohesion influence performance but task cohesion is mostly for the athletes who may be more competitive and take their sport really seriously whereas social cohesion is for athletes who may just play to have fun and enjoy the game rather than competing and winning the game.
Factors that effect group cohesion
There are factors that may effect group cohesion:
- team climate
- Carson's model of cohesion stated four factors;
-1. Environmental
-2. Personal
-3. Leadership
-4. Team
For a team to be working effectively in the right climate they would need:
- Good communication
-Team members know their roles
- Change is kept to a minimum
-Group has identity and goal
Team members must by helping by being responsible, resolving conflict, supporting each other and putting in 100% effort.
Carson's model of cohesion:
Environmental factors - groups that are closer in location and smaller groups tend to be more cohesive than larger groups. This is because team members may meet up regularly and interact which may help in forming relationships.
Personal factors - Individual characteristics of group members are important, this is because the group members may g=have similar opinions, commitment levels, backgrounds and shared goals and objectives.
Leadership factors - The leadership style that is used is important for the whole team. Behavior, communication styles and compatibility of the coach are key factors that affect group cohesion.
Team factors - The longer the period of time the group is together for the more cohesive is the group. The team may experience success and failures which may make the team more cohesive. By being involved in making decision this may have a huge impact on the whole group as it is increasing the cohesiveness of the group.
No comments:
Post a Comment